Profile

David Weber
As Director of the Center for Biomolecular Therapeutics (CBT) located within IBBR, Dr. Weber manages state-of-the-art scientific studies that investigate mechanisms involved in disease states and develops drugs to treat them. His laboratory is one of many in the CBT developing small-molecule inhibitors geared toward treating cancer, diabetes, and infectious disease.
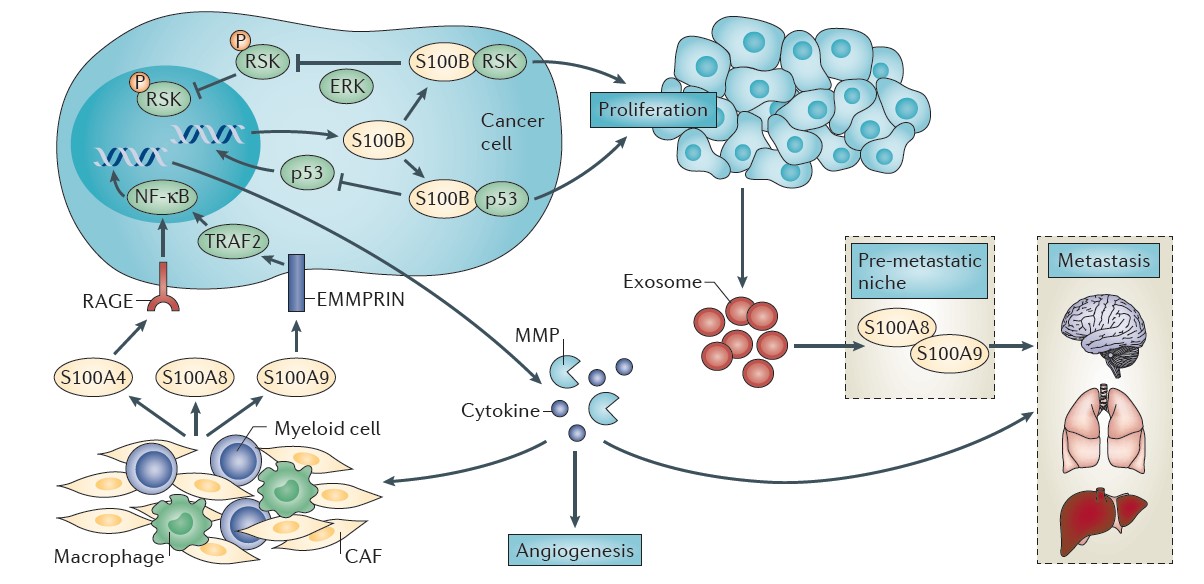
One such project involves studies of the structure, function, and inhibition of the S100 family of calcium-binding proteins. The Weber lab has shown that one particular S100 protein called S100B is not only an important marker for the prognosis of malignant melanoma patients, but that it also contributes to the disease state. Specifically, higher levels of S100B was shown to eliminate an important natural tumor suppressor called p53 (Figure 1). To address this problem, they developed small molecules inhibitors of S100B to restore active p53. Such molecules have the potential to help patients where other therapies are not effective, including cancer immunology approaches. To achieve this goal, structure-based drug-design technologies are used to develop experimental drugs that are more potent and safer than existing inhibitors and are being evaluated in malignant melanoma mouse models.
If successful, the next steps will be to develop such inhibitors safe for use in a human clinical trial with the long-range goal of helping provide new treatment options to malignant melanoma patients. Malignant melanoma is the fifth and seventh most common cancer among men and women, respectively, with more than 60,000 cases per year.
CBT Overview
CBT comprises seven research sections, each leveraging the intellectual capital of The University System of Maryland (USM) and an entrepreneurial, scientific environment to excel in aspects of therapeutic development and treatment. This combination delivers a comprehensive approach to the science of advancing human health, from discovery to therapeutic development.
Targeting infectious disease, cancer, diabetes, and neurological diseases, CBT researchers and scientists develop potential treatments to fight disease and improve quality of life. From target identification through testing, CBT uses a suite of technological and biomedical tools not found collectively in any other institution in the United States. Capitalizing on the depth and breadth of expertise found at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, and with close collaboration across University Systems of Maryland, CBT performs a number of services integral to the fight against disease, including world-renowned research in medicinal chemistry, structural biology, protein engineering, and biophysics.
Publications
- Bile Acids Are Potential Negative Allosteric Modulators of M1 Muscarinic Receptors.
- Hierarchical AF2RAVE for Multiconformation Virtual Screening Targeting S100 Ca2+-Binding Proteins.
- Pore formation by the CDTb component of the Clostridioides difficile binary toxin is Ca2+-dependent.
- High-Throughput Ligand Dissociation Kinetics Predictions Using Site Identification by Ligand Competitive Saturation.
- Thermal proteome profiling and proteome analysis using high-definition mass spectrometry demonstrate modulation of cholesterol biosynthesis by next-generation galeterone analog VNPP433-3β in castration-resistant prostate cancer.
- Detection of Putative Ligand Dissociation Pathways in Proteins Using Site-Identification by Ligand Competitive Saturation.
- Unveiling the intricate role of S100A1 in regulating RyR1 activity: A commentary on "Structural insights into the regulation of RyR1 by S100A1".
- Structural and Functional Insights into the Delivery Systems of Bacillus and Clostridial Binary Toxins.
- Deuterium spin relaxation of fractionally deuterated ribonuclease H using paired 475 and 950 MHz NMR spectrometers.
- Deciphering S100B Allosteric Signaling: The Role of a Peptide Target, TRTK-12, as an Ensemble Modulator.
- Dendritic Cell-Mediated Cross-Priming by a Bispecific Neutralizing Antibody Boosts Cytotoxic T Cell Responses and Protects Mice against SARS-CoV-2.
- Initial exploration of a novel fusion protein, IL-4/IL-34/IL-10, which promotes cardiac allograft survival mice through alloregulation.
- VNLG-152R and its deuterated analogs potently inhibit/repress triple/quadruple negative breast cancer of diverse racial origins in vitro and in vivo by upregulating E3 Ligase Synoviolin 1 (SYVN1) and inducing proteasomal degradation of MNK1/2.
- Salinization Dramatically Enhance the Anti-Prostate Cancer Efficacies of AR/AR-V7 and Mnk1/2 Molecular Glue Degraders, Galeterone and VNPP433-3β Which Outperform Docetaxel and Enzalutamide in CRPC CWR22Rv1 Xenograft Mouse Model.
- Transglutaminase 2 binds to the CD44v6 cytoplasmic domain to stimulate CD44v6/ERK1/2 signaling and maintain an aggressive cancer phenotype.
- Croquemort elicits activation of the immune deficiency pathway in ticks.
- Integrated Covalent Drug Design Workflow Using Site Identification by Ligand Competitive Saturation.
- Targeted Degradation of Androgen Receptor by VNPP433-3β in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Cells Implicates Interaction with E3 Ligase MDM2 Resulting in Ubiquitin-Proteasomal Degradation.
- Structure-Based Design of Potent Iminosugar Inhibitors of Endoplasmic Reticulum α-Glucosidase I with Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Activity.
- 1H, 13C, and 15N assignments of the mRNA binding protein hnRNP A18.
- Computer-Aided Drug Design: An Update.
- Novel AR/AR-V7 and Mnk1/2 Degrader, VNPP433-3β: Molecular Mechanisms of Action and Efficacy in AR-Overexpressing Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer In Vitro and In Vivo Models.
- Transcriptome profiling reveals that VNPP433-3β, the lead next-generation galeterone analog inhibits prostate cancer stem cells by downregulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition and stem cell markers.
- Nano-Assembly of Quisinostat and Biodegradable Macromolecular Carrier Results in Supramolecular Complexes with Slow-Release Capabilities.
- Sulforaphane covalently interacts with the transglutaminase 2 cancer maintenance protein to alter its structure and suppress its activity.
- Physiologically Relevant Free Ca2+ Ion Concentrations Regulate STRA6-Calmodulin Complex Formation via the BP2 Region of STRA6.
- The calcium-binding protein S100B reduces IL6 production in malignant melanoma via inhibition of RSK cellular signaling.
- An Extract of Taro (Colocasia esculenta) Mediates Potent Inhibitory Actions on Metastatic and Cancer Stem Cells by Tumor Cell-Autonomous and Immune-Dependent Mechanisms.
- Drug Delivery Systems: A Few Examples of Applications, Drug Cargoes, and Administration Routes.
- 1HN, 13C, and 15N backbone resonance assignments of the SET/TAF-1β/I2PP2A oncoprotein (residues 23-225).
- A method to improve quantitative radiotracing-based analysis of the in vivo biodistribution of drug carriers.
- The Importance of Therapeutically Targeting the Binary Toxin from Clostridioides difficile.
- Engineering subtilisin proteases that specifically degrade active RAS.
- Intracellular Delivery of Active Proteins by Polyphosphazene Polymers.
- Specificity of Molecular Fragments Binding to S100B versus S100A1 as Identified by NMR and Site Identification by Ligand Competitive Saturation (SILCS).
- Small molecules inhibitors of the heterogeneous ribonuclear protein A18 (hnRNP A18): a regulator of protein translation and an immune checkpoint.
- 1HN, 13C, and 15N resonance assignments of the Clostridioides difficile receptor binding domain 2 (CDTb, residues 757-876).
- Intertwined mechanisms define transport of anti-ICAM nanocarriers across the endothelium and brain delivery of a therapeutic enzyme.
- Correction to: 1HN, 13C, and 15N resonance assignments of human calmodulin bound to a peptide derived from the STRA6 vitamin A transporter (CaMBP2).
- Structure of the cell-binding component of the Clostridium difficile binary toxin reveals a di-heptamer macromolecular assembly.
- Galeterone and The Next Generation Galeterone Analogs, VNPP414 and VNPP433-3β Exert Potent Therapeutic Effects in Castration-/Drug-Resistant Prostate Cancer Preclinical Models In Vitro and In Vivo.
- An asymmetry that leads to activity.
- Second harmonic generation detection of Ras conformational changes and discovery of a small molecule binder.
- A temperature-dependent conformational shift in p38α MAPK substrate-binding region associated with changes in substrate phosphorylation profile.
- Alterations in Cellular Processes Involving Vesicular Trafficking and Implications in Drug Delivery.
- δ-Tocopherol Effect on Endocytosis and Its Combination with Enzyme Replacement Therapy for Lysosomal Disorders: A New Type of Drug Interaction?
- Unprecedently high targeting specificity toward lung ICAM-1 using 3DNA nanocarriers.
- 1HN, 13C, and 15N backbone resonance assignments of the human DNA ligase 3 DNA-binding domain (residues 257-477).
- The structural and biochemical impacts of monomerizing human acetylcholinesterase.
- Combining vascular targeting and the local first pass provides 100-fold higher uptake of ICAM-1-targeted vs untargeted nanocarriers in the inflamed brain.
- 1HN, 13C, and 15N resonance assignments of human calmodulin bound to a peptide derived from the STRA6 vitamin A transporter (CaMBP2).
- Targeting S100 Calcium-Binding Proteins with Small Molecule Inhibitors.
- Exploring protein-protein interactions using the site-identification by ligand competitive saturation methodology.
- Sibling rivalry: Males with more brothers develop larger testes.
- Loss of S100A1 expression leads to Ca2+ release potentiation in mutant mice with disrupted CaM and S100A1 binding to CaMBD2 of RyR1.
- Local extinction of the Asian tiger mosquito (Aedes albopictus) following rat eradication on Palmyra Atoll.
- Targeting superoxide dismutase to endothelial caveolae profoundly alleviates inflammation caused by endotoxin.
- Estimation of Skeletal Muscle Mass Relative to Adiposity Improves Prediction of Physical Performance and Incident Disability.
- Co-coating of receptor-targeted drug nanocarriers with anti-phagocytic moieties enhances specific tissue uptake versus non-specific phagocytic clearance.
- ICAM-1-Targeted Nanocarriers Attenuate Endothelial Release of Soluble ICAM-1, an Inflammatory Regulator.
- ICAM-1 targeting, intracellular trafficking, and functional activity of polymer nanocarriers coated with a fibrinogen-derived peptide for lysosomal enzyme replacement.
- Enhanced Delivery and Effects of Acid Sphingomyelinase by ICAM-1-Targeted Nanocarriers in Type B Niemann-Pick Disease Mice.
- Biodegradable "Smart" Polyphosphazenes with Intrinsic Multifunctionality as Intracellular Protein Delivery Vehicles.
- Lysosomal enzyme replacement therapies: Historical development, clinical outcomes, and future perspectives.
- The Activation of Protein Kinase A by the Calcium-Binding Protein S100A1 Is Independent of Cyclic AMP.
- X-ray crystal structure of human calcium-bound S100A1.
- Crystal structure of the human heterogeneous ribonucleoprotein A18 RNA-recognition motif.
- How Carrier Size and Valency Modulate Receptor-Mediated Signaling: Understanding the Link between Binding and Endocytosis of ICAM-1-Targeted Carriers.
- Structure of the STRA6 receptor for retinol uptake.
- Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells for Disease Modeling and Evaluation of Therapeutics for Niemann-Pick Disease Type A.
- Intra- and trans-cellular delivery of enzymes by direct conjugation with non-multivalent anti-ICAM molecules.
- Chitosan-Alginate Microcapsules Provide Gastric Protection and Intestinal Release of ICAM-1-Targeting Nanocarriers, Enabling GI Targeting In Vivo.
- (1)H(N), (13)C, and (15)N resonance assignments of the CDTb-interacting domain (CDTaBID) from the Clostridium difficile binary toxin catalytic component (CDTa, residues 1-221).
- Novel protein-inhibitor interactions in site 3 of Ca(2+)-bound S100B as discovered by X-ray crystallography.
- Size and targeting to PECAM vs ICAM control endothelial delivery, internalization and protective effect of multimolecular SOD conjugates.
- 1H, 13C, and 15N resonance assignments of an enzymatically active domain from the catalytic component (CDTa, residues 216-420) of a binary toxin from Clostridium difficile.
- Small Molecule Inhibitors of Ca(2+)-S100B Reveal Two Protein Conformations.
- Drug Delivery: Open Sesame Strategies for the One Thousand and One Body Barriers.
- A Comparative Study on the Alterations of Endocytic Pathways in Multiple Lysosomal Storage Disorders.
- DNA-Based Drug Carriers: The Paradox of a Classical "Cargo" Material Becoming a Versatile "Carrier" to Overcome Barriers in Drug Delivery.
- A piRNA-like small RNA interacts with and modulates p-ERM proteins in human somatic cells.
- Flow shear stress differentially regulates endothelial uptake of nanocarriers targeted to distinct epitopes of PECAM-1.
- Altered Clathrin-Independent Endocytosis in Type A Niemann-Pick Disease Cells and Rescue by ICAM-1-Targeted Enzyme Delivery.
- S100 proteins in cancer.
- Open challenges in magnetic drug targeting.
- Targeting, endocytosis, and lysosomal delivery of active enzymes to model human neurons by ICAM-1-targeted nanocarriers.
- Distinct subcellular trafficking resulting from monomeric vs multimeric targeting to endothelial ICAM-1: implications for drug delivery.
- Covalent small molecule inhibitors of Ca(2+)-bound S100B.
- A DNA-Device that Mediates Selective Endosomal Escape and Intracellular Delivery of Drugs and Biologicals.
- Clathrin-mediated endocytosis is impaired in type A-B Niemann-Pick disease model cells and can be restored by ICAM-1-mediated enzyme replacement.
- Combination-targeting to multiple endothelial cell adhesion molecules modulates binding, endocytosis, and in vivo biodistribution of drug nanocarriers and their therapeutic cargoes.
- Enhancing biodistribution of therapeutic enzymes in vivo by modulating surface coating and concentration of ICAM-1-targeted nanocarriers.
- Complex formation between S100B protein and the p90 ribosomal S6 kinase (RSK) in malignant melanoma is calcium-dependent and inhibits extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)-mediated phosphorylation of RSK.
- Specific binding, uptake, and transport of ICAM-1-targeted nanocarriers across endothelial and subendothelial cell components of the blood-brain barrier.
- Small G proteins Rac1 and Ras regulate serine/threonine protein phosphatase 5 (PP5)·extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) complexes involved in the feedback regulation of Raf1.
- Structure of the S100A4/myosin-IIA complex.
- Biological functionalization of drug delivery carriers to bypass size restrictions of receptor-mediated endocytosis independently from receptor targeting.
- Models and methods to evaluate transport of drug delivery systems across cellular barriers.
- In vivo performance of polymer nanocarriers dually-targeted to epitopes of the same or different receptors.
- In vivo screening of S100B inhibitors for melanoma therapy.
- Structure-Based Discovery of a Novel Pentamidine-Related Inhibitor of the Calcium-Binding Protein S100B.
- The evolution of S100B inhibitors for the treatment of malignant melanoma.
- Impact of a rapid peptide nucleic acid fluorescence in situ hybridization assay on treatment of Candida infections.
- Comparative binding, endocytosis, and biodistribution of antibodies and antibody-coated carriers for targeted delivery of lysosomal enzymes to ICAM-1 versus transferrin receptor.
- Acute and chronic shear stress differently regulate endothelial internalization of nanocarriers targeted to platelet-endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1.
- Biodistribution and endocytosis of ICAM-1-targeting antibodies versus nanocarriers in the gastrointestinal tract in mice.
- Target binding to S100B reduces dynamic properties and increases Ca(2+)-binding affinity for wild type and EF-hand mutant proteins.
- Challenges in design and characterization of ligand-targeted drug delivery systems.
- Transport of nanocarriers across gastrointestinal epithelial cells by a new transcellular route induced by targeting ICAM-1.
- Strategies for delivery of therapeutics into the central nervous system for treatment of lysosomal storage disorders.
- Endothelial targeting of polymeric nanoparticles stably labeled with the PET imaging radioisotope iodine-124.
- Effect of thiol pendant conjugates on plasmid DNA binding, release, and stability of polymeric delivery vectors.
- Intercellular adhesion molecule 1 engagement modulates sphingomyelinase and ceramide, supporting uptake of drug carriers by the vascular endothelium.
- A fibrinogen-derived peptide provides intercellular adhesion molecule-1-specific targeting and intraendothelial transport of polymer nanocarriers in human cell cultures and mice.
- Targeting zymogen activation to control the matriptase-prostasin proteolytic cascade.
- S100A1 (S100 calcium binding protein A1).
- Effect of flow on endothelial endocytosis of nanocarriers targeted to ICAM-1.
- Enhanced delivery of α-glucosidase for Pompe disease by ICAM-1-targeted nanocarriers: comparative performance of a strategy for three distinct lysosomal storage disorders.
- Endothelial targeting of antibody-decorated polymeric filomicelles.
- Two functional S100A4 monomers are necessary for regulating nonmuscle myosin-IIA and HCT116 cell invasion.
- Modulation of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ release in skeletal muscle expressing ryanodine receptor impaired in regulation by calmodulin and S100A1.
- Targeting delivery of drugs in the vascular system.
- Effect of Glycocalyx on Drug Delivery Carriers Targeted to Endothelial Cells.
- In vitro screening and structural characterization of inhibitors of the S100B-p53 interaction.
- Enhanced endothelial delivery and biochemical effects of α-galactosidase by ICAM-1-targeted nanocarriers for Fabry disease.
- Optimizing endothelial targeting by modulating the antibody density and particle concentration of anti-ICAM coated carriers.
- The Calcium-Dependent Interaction of S100B with Its Protein Targets.
- The calcium-binding protein S100B down-regulates p53 and apoptosis in malignant melanoma.
- Phenothiazines inhibit S100A4 function by inducing protein oligomerization.
- The calcium-dependent interaction between S100B and the mitochondrial AAA ATPase ATAD3A and the role of this complex in the cytoplasmic processing of ATAD3A.
- New biotechnological and nanomedicine strategies for treatment of lysosomal storage disorders.
- The effects of CapZ peptide (TRTK-12) binding to S100B-Ca2+ as examined by NMR and X-ray crystallography.
- S100A1: Structure, Function, and Therapeutic Potential.
- Deletion of PTEN promotes tumorigenic signaling, resistance to anoikis, and altered response to chemotherapeutic agents in human mammary epithelial cells.
- Flow dynamics, binding and detachment of spherical carriers targeted to ICAM-1 on endothelial cells.
- Augmentation of Cav1 channel current and action potential duration after uptake of S100A1 in sympathetic ganglion neurons.
- Small molecules bound to unique sites in the target protein binding cleft of calcium-bound S100B as characterized by nuclear magnetic resonance and X-ray crystallography.
- Solution structure of S100A1 bound to the CapZ peptide (TRTK12).
- Refinement of the solution structure and dynamic properties of Ca(2+)-bound rat S100B.
- Oxygen microscopy by two-photon-excited phosphorescence.
- S100A1 and calmodulin compete for the same binding site on ryanodine receptor.
- Differential intra-endothelial delivery of polymer nanocarriers targeted to distinct PECAM-1 epitopes.
- Divalent metal ion complexes of S100B in the absence and presence of pentamidine.
- Control of endothelial targeting and intracellular delivery of therapeutic enzymes by modulating the size and shape of ICAM-1-targeted carriers.
- Extracellular proteolytic activities expressed by Bacillus pumilus isolated from endodontic and periodontal lesions.
- Structure of Ca2+-bound S100A4 and its interaction with peptides derived from nonmuscle myosin-IIA.
- Delivery of acid sphingomyelinase in normal and niemann-pick disease mice using intercellular adhesion molecule-1-targeted polymer nanocarriers.
- RhoA activation and actin reorganization involved in endothelial CAM-mediated endocytosis of anti-PECAM carriers: critical role for tyrosine 686 in the cytoplasmic tail of PECAM-1.
- Inhibition of protein-protein interactions with low molecular weight compounds.
- S100A1 binds to the calmodulin-binding site of ryanodine receptor and modulates skeletal muscle excitation-contraction coupling.
- In vivo imaging of 64Cu-labeled polymer nanoparticles targeted to the lung endothelium.
- Restriction endonuclease inhibitor IPI* of bacteriophage T4: a novel structure for a dedicated target.
- Getting a grip on calcium regulation.
- Solution structure of the novel dispersin protein of enteroaggregative Escherichia coli.
- A search for inhibitors of S100B, a member of the S100 family of calcium-binding proteins.
- Recognition of the tumor suppressor protein p53 and other protein targets by the calcium-binding protein S100B.
- Advanced drug delivery systems that target the vascular endothelium.
- An N-terminal sequence targets and tethers Na+ pump alpha2 subunits to specialized plasma membrane microdomains.
- Post-transcriptional regulation of thioredoxin by the stress inducible heterogenous ribonucleoprotein A18.
- Endothelial targeting of high-affinity multivalent polymer nanocarriers directed to intercellular adhesion molecule 1.
- Control of intracellular trafficking of ICAM-1-targeted nanocarriers by endothelial Na+/H+ exchanger proteins.
- Design of Inhibitors for S100B.
- S100A4, a mediator of metastasis.
- Refinement of the solution structure of rat olfactory marker protein (OMP).
- The three-dimensional solution structure of Ca(2+)-bound S100A1 as determined by NMR spectroscopy.
- Lysosomal enzyme delivery by ICAM-1-targeted nanocarriers bypassing glycosylation- and clathrin-dependent endocytosis.
- Backbone dynamics of the olfactory marker protein as studied by 15N NMR relaxation measurements.
- Calcium-binding properties of wild-type and EF-hand mutants of S100B in the presence and absence of a peptide derived from the C-terminal negative regulatory domain of p53.
- Solution structure of zinc- and calcium-bound rat S100B as determined by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
- Solution NMR structure of S100B bound to the high-affinity target peptide TRTK-12.
- Solution structure of human Mts1 (S100A4) as determined by NMR spectroscopy.
- Olfactory marker protein (OMP) exhibits a beta-clam fold in solution: implications for target peptide interaction and olfactory signal transduction.
- Three-dimensional solution structure of the calcium-signaling protein apo-S100A1 as determined by NMR.
