Robert Brinson
Research Chemist
Brinson Group (240) 314-6336 rbrinson@umd.eduDr. Robert Brinson uses biophysical measurements to define the structure and dynamics of nucleic acids, proteins, and glycoproteins, with a specific focus on biotherapeutics. In particular, he seeks to harmonize and to translate nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) methods for biopharmaceutical applications and to push the limits of NMR methodologies to define the critical quality attributes of higher order structure for protein drug products.
CURRENT RESEARCH
2D-NMR Method Development for Biopharmaceutical Structural Assessment
Techniques for the facile characterization of higher order structure of biotherapeutics are in great demand by the pharmaceutical industry. NMR spectroscopy provides structural information about proteins at atomic resolution as individual peak positions in ‘fingerprint’ amide or methyl NMR spectra are sensitive to structure. These peaks can serve as spectral indicators for establishing consistency in drug manufacturing, assessing the stability of drug formulations, detecting process-related drug product variations, and determining biosimilarity to innovator reference products. However, limits on sensitivity, molecular size, sample volumes, and the perceived need for stable-isotope enrichment have restrained widespread use of NMR in the biopharmaceutical industry. Recent advances in NMR hardware, acquisition methods, and new approaches for data analyses have greatly ameliorated these limitations. Two-dimensional (2D) 1H-13C and 1H-15N correlated spectra can now be collected on biologics, including monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), at natural isotopic abundance. Furthermore, in collaboration with the Mathematical Analysis and Modeling Group at NIST, Dr. Brinson develops chemometric analyses for the extraction of meaningful information from many 2D spectra. Together, the researchers aim to develop best practices based on the type of analyses needed for a given protein therapeutic sample set.
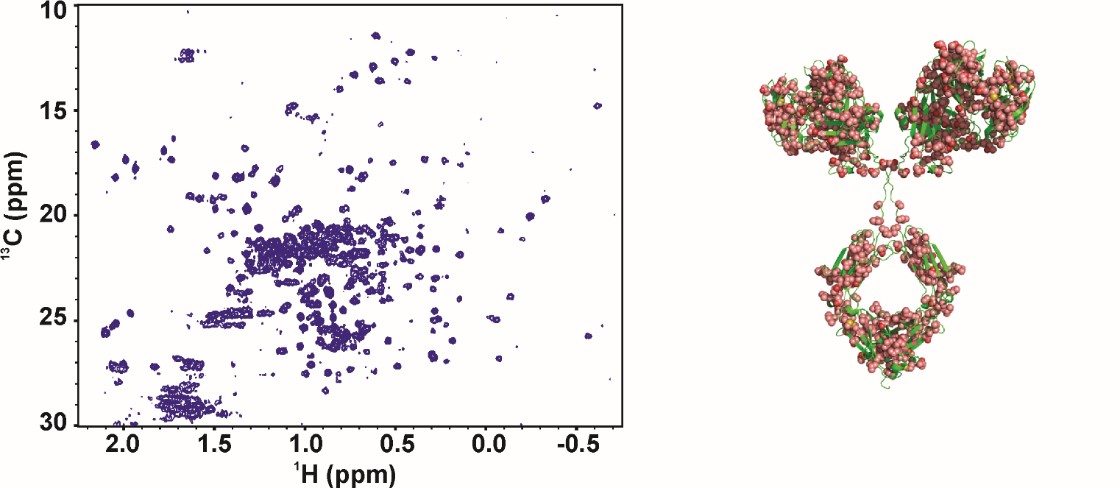
Harmonization of the 2D-NMR method through an International Interlaboratory Study
The NISTmAb Interlaboratory NMR Study is a joint effort among 25 organizations to evaluate the performance of 2D heteronuclear NMR for use in characterizing the high order structure of proteins, with the aim of supporting the use of NMR to characterize biologic therapeutics. Researchers in nine countries, with equal representation from industrial, governmental, and academic laboratories, acquired 451 1H-13C-methyl and 1H-15N-amide 2D NMR correlation spectra using different acquisition methods and instruments. Spectra were collected on both the Fab antibody domain derived from the IgG1κ NIST monoclonal antibody (NISTmAb) and a U-15N, 20%-13C labeled NIST-Fab system suitability sample. Chemometric analyses, using multivariate statistical methods, allowed benchmarking of the precision and robustness of the NMR measurements. The complete data package is available at www.ibbr.umd.edu/groups/nistmab-nmr.
Publications
- Hydrogen-Deuterium Exchange Dynamics of NISTmAb Measured by Small Angle Neutron Scattering.
- Backbone NMR assignment of the yeast expressed Fab fragment of the NISTmAb reference antibody.
- Correlated analytical and functional evaluation of higher order structure perturbations from oxidation of NISTmAb.
- Structural Fingerprinting of Antisense Oligonucleotide Therapeutics by Solution NMR Spectroscopy.
- Interlaboratory Studies Using the NISTmAb to Advance Biopharmaceutical Structural Analytics.
- Structural Fingerprinting of Short Interfering RNA Therapeutics by Solution Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy.
- Excipient Innovation Through Precompetitive Research.
- Highly conserved s2m element of SARS-CoV-2 dimerizes via a kissing complex and interacts with host miRNA-1307-3p.
- Practical Applications of NMR to Solve Real-World Problems.
- Grand Challenges in Pharmaceutical Research Series: Ridding the Cold Chain for Biologics.
- Crystal Structure of a Bivalent Antibody Fab Fragment.
- Principal component analysis for automated classification of 2D spectra and interferograms of protein therapeutics: influence of noise, reconstruction details, and data preparation.
- Assessment of the Higher-Order Structure of Formulated Monoclonal Antibody Therapeutics by 2D Methyl Correlated NMR and Principal Component Analysis.
- Best Practices in Utilization of 2D-NMR Spectral Data as the Input for Chemometric Analysis in Biopharmaceutical Applications.
- Chemometric Outlier Classification of 2D-NMR Spectra to Enable Higher Order Structure Characterization of Protein Therapeutics.
- Structure and Dynamics of a Site-Specific Labeled Fc Fragment with Altered Effector Functions.
- Characterization of the internal translation initiation region in monoclonal antibodies expressed in Escherichia coli.
- 2D J-correlated proton NMR experiments for structural fingerprinting of biotherapeutics.
- Structural insights into DNA-stabilized silver clusters.
- Enabling adoption of 2D-NMR for the higher order structure assessment of monoclonal antibody therapeutics.
- Platform development for expression and purification of stable isotope labeled monoclonal antibodies in Escherichia coli.
- Non-Uniform Sampling for All: More NMR Spectral Quality, Less Measurement Time.
- Precision and robustness of 2D-NMR for structure assessment of filgrastim biosimilars.
- Applying Thymine Isostere 2,4-Difluoro-5-Methylbenzene as a NMR Assignment Tool and Probe of Homopyrimidine/Homopurine Tract Structural Dynamics.
- Application of Natural Isotopic Abundance ¹H-¹³C- and ¹H-¹⁵N-Correlated Two-Dimensional NMR for Evaluation of the Structure of Protein Therapeutics.
- Observation of heavy atom effects in the development of water soluble caged 4-hydroxy-trans-2-nonenal.
- Structural probing of the HIV-1 polypurine tract RNA:DNA hybrid using classic nucleic acid ligands.
- High-resolution NMR analysis of the conformations of native and base analog substituted retroviral and LTR-retrotransposon PPT primers.
