William Bentley
Distinguished University Professor
Bentley Group (301) 405-4321 bentley@umd.eduDr. William E. Bentley develops and uses molecular tools to engineer cells for enhanced function (synthetic biology) and to open “communication” pathways for innovative device design and fabrication (bioelectronics). His laboratory has engineered cells and small consortia of cells to execute advanced functions such as detecting and killing pathogens. His lab has also adapted natural bacterial signaling pathways to build components and systems that enable bidirectional communication between devices and biological systems.
CURRENT RESEARCH
Metabolic and Biomolecular Engineering – Quorum Sensing and Cell Networks
The Bentley Lab creates and uses molecular tools to understand the regulation of genetic circuits during applied stresses, and to gain near real-time information on the dynamics of metabolites, genes, proteins, and protein assemblies in targeted circuits. They use systems biology and synthetic biology approaches to alter the intracellular environment to improve cellular processes.
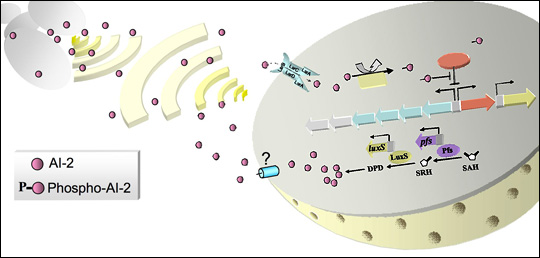 Many projects in the lab involve “quorum sensing” (QS), a signal transduction pathway of cell-to-cell communication about population levels that regulates cell behavior and enables individual bacteria to act with multicellularity. The Bentley Lab was the first group to use QS signaling to develop a means to control bacterial subpopulations and sort quantized quorums (Servinsky et al. 2015, ISME Journal). More recently, they exploited these signaling pathways that control individual and groups of cells to engineer bacteria to seek out and kill pathogens in the GI tract of mice (Hwang et al. 2017, Nature Comm). Here, the cells themselves are functioning products of synthetic biology, as they recognize, compute, actuate, and deliver -- all in a programmed manner.
Many projects in the lab involve “quorum sensing” (QS), a signal transduction pathway of cell-to-cell communication about population levels that regulates cell behavior and enables individual bacteria to act with multicellularity. The Bentley Lab was the first group to use QS signaling to develop a means to control bacterial subpopulations and sort quantized quorums (Servinsky et al. 2015, ISME Journal). More recently, they exploited these signaling pathways that control individual and groups of cells to engineer bacteria to seek out and kill pathogens in the GI tract of mice (Hwang et al. 2017, Nature Comm). Here, the cells themselves are functioning products of synthetic biology, as they recognize, compute, actuate, and deliver -- all in a programmed manner.
Biofabrication Engineering of Biological Signaling - bBIOS
The Bentley Lab is engaged in a multidisciplinary effort to create systems that serve to bridge the communication gap between biological systems and electronic microfabricated devices. Biology “communicates” via small molecule signaling (e.g. QS above) and ion flow, but devices are programmed with electrons, leading to a problem of translation. Dr. Bentley’s group employs the biopolymer chitosan as a “smart” stimuli-responsive interface. 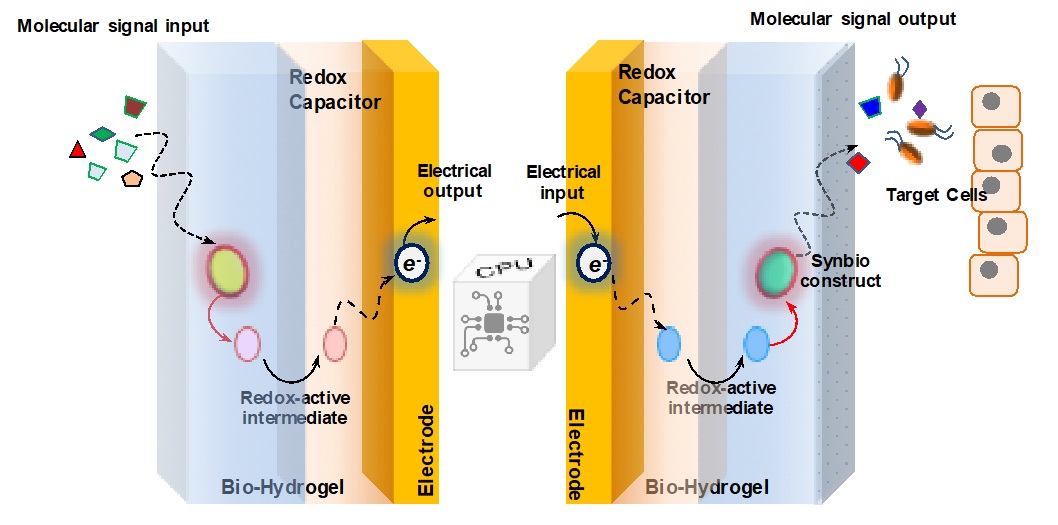
For example, the group developed a means to electronically assemble and control the activity of a two-enzyme biosynthetic pathway that leads to a bacterial QS signal molecule (Gordonov et al. 2014, Nature Nanotech). This showed for the first time that one can electrically connect to and control biological behavior. A signal molecule generated and controlled on-chip affected behavioral phenotype at the population level,
More recently, they demonstrated for the first time direct electrical actuation of gene expression in bacteria. They exploited redox signaling to actuate in a reversible manner expression of several genes in E. coli, including those that synthesize a native QS signal molecule. This molecule, in turn, actuated gene expression in neighboring cells. Hence, electrically programmed cells were made to stimulate signaling via native biological means. (Tshirhart et al. 2017, Nature Comm). For more information, visit the Maryland Biochip Collaborative website.
The Bentley group anticipates developing new tools for deciphering the presence of pathogens and for understanding and treatment of metabolic diseases, cancer, and hemorrhagic shock.
Publications
- Genetically-Programmed Hypervesiculation of Lactiplantibacillus Plantarum Increases Production of Bacterial Extracellular Vesicles with Therapeutic Efficacy in a Preclinical Inflammatory Bowel Disease Model.
- Scrambling Signal Modularity in Bottom-up Assembled Synthetic Pseudomonas Consortia Reveals Robust Information Transfer.
- Electrochemistry as a Tool for Redox-Based Bio-Information Processing.
- Genetically-programmed Hypervesiculation of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Increases Production of Bacterial Extracellular Vesicles with Therapeutic Efficacy in a Preclinical Inflammatory Bowel Disease Model.
- Measuring oxidative stress by the iridium reducing capacity assay (Ir-RCA).
- Yersinia pseudotuberculosis growth arrest during type-III secretion system expression is associated with altered ribosomal protein expression and decreased gentamicin susceptibility.
- 3D nanoprinting of PDMS microvessels with tailored tortuosity and microporosity via direct laser writing.
- 3D Printed Spectroelectrochemical Platform for Redox-Based Bioelectronics.
- Proline-Selective Electrochemiluminescence Detecting a Single Amino Acid Variation Between A1 and A2 β-Casein Containing Milks.
- Detecting features of antibody structure through their mediator-accessible redox activities.
- Biomimetic Redox Capacitor To Control the Flow of Electrons.
- Yersinia pseudotuberculosis growth arrest during type-III secretion system expression is associated with altered ribosomal protein expression and decreased gentamicin susceptibility.
- Electrobiofabrication of antibody sensor interfaces within a 3D printed device yield rapid and robust electrochemical measurements of titer and glycan structure.
- Redox-mediated Biomolecular information transfer in single electrogenetic biological cells.
- Pilot study indicates that a gluten-free diet lowers oxidative stress for gluten-sensitive persons with schizophrenia.
- Redox active plant phenolic, acetosyringone, for electrogenetic signaling.
- Excite the unexcitable: engineering cells and redox signaling for targeted bioelectronic control.
- Redox-enabled electronic interrogation and feedback control of hierarchical and networked biological systems.
- High performance anion exchange chromatography purification of probiotic bacterial extracellular vesicles enhances purity and anti-inflammatory efficacy.
- High performance anion exchange chromatography purification of probiotic bacterial extracellular vesicles enhances purity and anti-inflammatory efficacy.
- Electro-Biofabrication. Coupling Electrochemical and Biomolecular Methods to Create Functional Bio-Based Hydrogels.
- Cell-Like Capsules with "Smart" Compartments.
- Electrogenetic signaling and information propagation for controlling microbial consortia via programmed lysis.
- Highly stable, antiviral, antibacterial cotton textiles via molecular engineering.
- Enhanced electrochemical measurement of β-galactosidase activity in whole cells by coexpression of lactose permease, LacY.
- Protein G: β-galactosidase fusion protein for multi-modal bioanalytical applications.
- Quorum sensing componentry opens new lines of communication.
- Bacterial chemotaxis in static gradients quantified in a biopolymer membrane-integrated microfluidic platform.
- Network-based redox communication between abiotic interactive materials.
- Electrogenetic Signal Transmission and Propagation in Coculture to Guide Production of a Small Molecule, Tyrosine.
- Parsed synthesis of pyocyanin via co-culture enables context-dependent intercellular redox communication.
- 3D-Printed electrochemical sensor-integrated transwell systems.
- Editorial overview: Bioanalytical tools, techniques, and trailblazers offer insight to drive bioprocess development.
- Electrochemical measurement of serotonin by Au-CNT electrodes fabricated on microporous cell culture membranes.
- Association of acute psychosocial stress with oxidative stress: Evidence from serum analysis.
- Mediated electrochemistry for redox-based biological targeting: entangling sensing and actuation for maximizing information transfer.
- A Redox-Based Autoinduction Strategy to Facilitate Expression of 5xCys-Tagged Proteins for Electrobiofabrication.
- Electronic signals are electrogenetically relayed to control cell growth and co-culture composition.
- Mediated Electrochemical Probing: A Systems-Level Tool for Redox Biology.
- Single-Step Synthesis of Alginate Microgels Enveloped with a Covalent Polymeric Shell: A Simple Way to Protect Encapsulated Cells.
- Bacterial Extracellular Vesicles and the Gut-Microbiota Brain Axis: Emerging Roles in Communication and Potential as Therapeutics.
- Simple, rapidly electroassembled thiolated PEG-based sensor interfaces enable rapid interrogation of antibody titer and glycosylation.
- Interactive Materials for Bidirectional Redox-Based Communication.
- Bioelectronic control of a microbial community using surface-assembled electrogenetic cells to route signals.
- Redox Electrochemistry to Interrogate and Control Biomolecular Communication.
- Homologous Quorum Sensing Regulatory Circuit: A Dual-Input Genetic Controller for Modulating Quorum Sensing-Mediated Protein Expression in E. coli.
- Transglutaminase-mediated assembly of multi-enzyme pathway onto TMV brush surfaces for synthesis of bacterial autoinducer-2.
- A redox-based electrogenetic CRISPR system to connect with and control biological information networks.
- The importance and future of biochemical engineering.
- Synthetic Biology for Manipulating Quorum Sensing in Microbial Consortia.
- A Coculture Based Tyrosine-Tyrosinase Electrochemical Gene Circuit for Connecting Cellular Communication with Electronic Networks.
- Quorum Sensing Communication: Molecularly Connecting Cells, Their Neighbors, and Even Devices.
- Redox Is a Global Biodevice Information Processing Modality.
- Catechol-Based Capacitor for Redox-Linked Bioelectronics.
- Microsystems for biofilm characterization and sensing - A review.
- Rapid Electroformation of Biopolymer Gels in Prescribed Shapes and Patterns: A Simpler Alternative to 3-D Printing.
- Bacterial co-culture with cell signaling translator and growth controller modules for autonomously regulated culture composition.
- Pro- and Anti-oxidant Properties of Redox-Active Catechol-Chitosan Films.
- Validation of oxidative stress assay for schizophrenia.
- Engineering Escherichia coli for enhanced sensitivity to the autoinducer-2 quorum sensing signal.
- Bacteria Floc, but Do They Flock? Insights from Population Interaction Models of Quorum Sensing.
- Erratum: Catechol-Based Hydrogel for Chemical Information Processing. Biomimetics 2017, 2, 11.
- Redox-Based Synthetic Biology Enables Electrochemical Detection of the Herbicides Dicamba and Roundup via Rewired Escherichia coli.
- Electrobiofabrication: electrically based fabrication with biologically derived materials.
- Plasmid-encoded protein attenuates Escherichia coli swimming velocity and cell growth, not reprogrammed regulatory functions.
- Coupling Self-Assembly Mechanisms to Fabricate Molecularly and Electrically Responsive Films.
- Biomimetic and Bioinspired Biotechnology.
- A platform of genetically engineered bacteria as vehicles for localized delivery of therapeutics: Toward applications for Crohn's disease.
- The 2018 Young Innovators of Cellular and Molecular Bioengineering.
- Selective assembly and functionalization of miniaturized redox capacitor inside microdevices for microbial toxin and mammalian cell cytotoxicity analyses.
- Flexible Platform for In Situ Impedimetric Detection and Bioelectric Effect Treatment of Escherichia Coli Biofilms.
- An immune magnetic nano-assembly for specifically amplifying intercellular quorum sensing signals.
- A new design for an artificial cell: polymer microcapsules with addressable inner compartments that can harbor biomolecules, colloids or microbial species.
- Development of Cell-Based Sentinels for Nitric Oxide: Ensuring Marker Expression and Unimodality.
- Radical Scavenging Activities of Biomimetic Catechol-Chitosan Films.
- Evidence of link between quorum sensing and sugar metabolism in Escherichia coli revealed via cocrystal structures of LsrK and HPr.
- Catechol-chitosan redox capacitor for added amplification in electrochemical immunoanalysis.
- Focusing quorum sensing signalling by nano-magnetic assembly.
- Electrodeposition of a magnetic and redox-active chitosan film for capturing and sensing metabolic active bacteria.
- Engineering bacterial motility towards hydrogen-peroxide.
- Biofabricating Functional Soft Matter Using Protein Engineering to Enable Enzymatic Assembly.
- Signal processing approach to probe chemical space for discriminating redox signatures.
- Site-specific immobilization of endoglycosidases for streamlined chemoenzymatic glycan remodeling of antibodies.
- Modification and Assembly of a Versatile Lactonase for Bacterial Quorum Quenching.
- Enhanced expression of a biosimilar monoclonal antibody with a novel NS0 platform.
- Electrical Programming of Soft Matter: Using Temporally Varying Electrical Inputs To Spatially Control Self Assembly.
- Connecting Biology to Electronics: Molecular Communication via Redox Modality.
- Spectroelectrochemical Reverse Engineering DemonstratesThat Melanin's Redox and Radical Scavenging Activities Are Linked.
- Microscale Bioreactors for in situ characterization of GI epithelial cell physiology.
- The Analgesic Acetaminophen and the Antipsychotic Clozapine Can Each Redox-Cycle with Melanin.
- A simple and reusable bilayer membrane-based microfluidic device for the study of gradient-mediated bacterial behaviors.
- An Integrated Microsystem for Real-Time Detection and Threshold-Activated Treatment of Bacterial Biofilms.
- Incorporating LsrK AI-2 quorum quenching capability in a functionalized biopolymer capsule.
- Controlling localization of Escherichia coli populations using a two-part synthetic motility circuit: An accelerator and brake.
- Catechol-Based Hydrogel for Chemical Information Processing.
- Engineered probiotic Escherichia coli can eliminate and prevent Pseudomonas aeruginosa gut infection in animal models.
- Microfluidic Arrayed Lab-On-A-Chip for Electrochemical Capacitive Detection of DNA Hybridization Events.
- Two-Way Chemical Communication between Artificial and Natural Cells.
- TumbleScore: Run and tumble analysis for low frame-rate motility videos.
- Electronic control of gene expression and cell behaviour in Escherichia coli through redox signalling.
- Electrochemical reverse engineering: A systems-level tool to probe the redox-based molecular communication of biology.
- Redox Probing for Chemical Information of Oxidative Stress.
- Mathematical model of LsrR-binding and derepression in Escherichia coli K12.
- Insightful directed evolution of Escherichia coli quorum sensing promoter region of the lsrACDBFG operon: a tool for synthetic biology systems and protein expression.
- Using a Redox Modality to Connect Synthetic Biology to Electronics: Hydrogel-Based Chemo-Electro Signal Transduction for Molecular Communication.
- A Facile Two-Step Enzymatic Approach for Conjugating Proteins to Polysaccharide Chitosan at an Electrode Interface.
- Modular construction of multi-subunit protein complexes using engineered tags and microbial transglutaminase.
- Fusing Sensor Paradigms to Acquire Chemical Information: An Integrative Role for Smart Biopolymeric Hydrogels.
- Autoinducer-2 analogs and electric fields - an antibiotic-free bacterial biofilm combination treatment.
- Constructing "quantized quorums" to guide emergent phenotypes through quorum quenching capsules.
- Data on biochemical fluxes generated from biofabricated enzyme complexes assembled through engineered tags and microbial transglutaminase.
- Conferring biological activity to native spider silk: A biofunctionalized protein-based microfiber.
- Electro-molecular Assembly: Electrical Writing of Information into an Erasable Polysaccharide Medium.
- Electrochemical Probing through a Redox Capacitor To Acquire Chemical Information on Biothiols.
- Enhancing Intercellular Coordination: Rewiring Quorum Sensing Networks for Increased Protein Expression through Autonomous Induction.
- Paraquat-Melanin Redox-Cycling: Evidence from Electrochemical Reverse Engineering.
- Networking biofabricated systems through molecular communication.
- Quorum Sensing Desynchronization Leads to Bimodality and Patterned Behaviors.
- Gene Silencing in Insect Cells Using RNAi.
- Tubular Bioreactor for Probing Baculovirus Infection and Protein Production.
- Evaluating Baculovirus Infection Using Green Fluorescent Protein and Variants.
- Electrochemical Fabrication of Functional Gelatin-Based Bioelectronic Interface.
- Editorial Overview: Synthetic biology hybrids - a golden age of pathway engineering.
- Colloidal Properties of Nanoerythrosomes Derived from Bovine Red Blood Cells.
- Reverse Engineering Applied to Red Human Hair Pheomelanin Reveals Redox-Buffering as a Pro-Oxidant Mechanism.
- Electrochemical Measurement of the β-Galactosidase Reporter from Live Cells: A Comparison to the Miller Assay.
- Functionalizing Soft Matter for Molecular Communication.
- Nano-guided cell networks as conveyors of molecular communication.
- Effect of electrical energy on the efficacy of biofilm treatment using the bioelectric effect.
- A 'bioproduction breadboard': programming, assembling, and actuating cellular networks.
- Directed assembly of a bacterial quorum.
- Self-assembly with orthogonal-imposed stimuli to impart structure and confer magnetic function to electrodeposited hydrogels.
- Rational design of 'controller cells' to manipulate protein and phenotype expression.
- Bacterial secretions of nonpathogenic Escherichia coli elicit inflammatory pathways: a closer investigation of interkingdom signaling.
- Distal modulation of bacterial cell-cell signalling in a synthetic ecosystem using partitioned microfluidics.
- Geminal dihalogen isosteric replacement in hydrated AI-2 affords potent quorum sensing modulators.
- Isolated perioperative hypertension: clinical implications & contemporary treatment strategies.
- A controlled microfluidic electrochemical lab-on-a-chip for label-free diffusion-restricted DNA hybridization analysis.
- A microfluidic-based electrochemical biochip for label-free DNA hybridization analysis.
- Rapid and repeatable redox cycling of an insoluble dietary antioxidant: electrochemical analysis.
- Electronic modulation of biochemical signal generation.
- Integrating artificial with natural cells to translate chemical messages that direct E. coli behaviour.
- Information processing through a bio-based redox capacitor: signatures for redox-cycling.
- Context-dependent redox properties of natural phenolic materials.
- Coding for hydrogel organization through signal guided self-assembly.
- Compartmentalized multilayer hydrogel formation using a stimulus-responsive self-assembling polysaccharide.
- Redox-capacitor to connect electrochemistry to redox-biology.
- Evolved Quorum sensing regulator, LsrR, for altered switching functions.
- Crystal structures of the LsrR proteins complexed with phospho-AI-2 and two signal-interrupting analogues reveal distinct mechanisms for ligand recognition.
- Tuning cell cycle of insect cells for enhanced protein production.
- Materials science. Nature's other self-assemblers.
- Investigating polymer thiolation in gene delivery.
- Optically clear alginate hydrogels for spatially controlled cell entrapment and culture at microfluidic electrode surfaces.
- Autonomous bacterial localization and gene expression based on nearby cell receptor density.
- Reverse engineering to suggest biologically relevant redox activities of phenolic materials.
- Amplified and in situ detection of redox-active metabolite using a biobased redox capacitor.
- Biofabricated film with enzymatic and redox-capacitor functionalities to harvest and store electrons.
- AI-2 analogs and antibiotics: a synergistic approach to reduce bacterial biofilms.
- Gene network homology in prokaryotes using a similarity search approach: queries of quorum sensing signal transduction.
- Glucose oxidase-mediated gelation: a simple test to detect glucose in food products.
- Encapsulated fusion protein confers "sense and respond" activity to chitosan-alginate capsules to manipulate bacterial quorum sensing.
- Bridging the bio-electronic interface with biofabrication.
- A microfluidic-based electrochemical biochip for label-free diffusion-restricted DNA hybridization analysis.
- Biofabrication of stratified biofilm mimics for observation and control of bacterial signaling.
- Altering the communication networks of multispecies microbial systems using a diverse toolbox of AI-2 analogues.
- Electrodeposition of a biopolymeric hydrogel: potential for one-step protein electroaddressing.
- Integrated biofabrication for electro-addressed in-film bioprocessing.
- Pathway engineering via quorum sensing and sRNA riboregulators-interconnected networks and controllers.
- Developing next generation antimicrobials by intercepting AI-2 mediated quorum sensing.
- Coupling electrodeposition with layer-by-layer assembly to address proteins within microfluidic channels.
- LsrR quorum sensing "switch" is revealed by a bottom-up approach.
- Effects on membrane lateral pressure suggest permeation mechanisms for bacterial quorum signaling molecules.
- Biofabrication of chitosan-silver composite SERS substrates enabling quantification of adenine by a spectroscopic shift.
- Microfluidic electrochemical sensor array for characterizing protein interactions with various functionalized surfaces.
- Biocompatible multi-address 3D cell assembly in microfluidic devices using spatially programmable gel formation.
- Electroaddressing agarose using Fmoc-phenylalanine as a temporary scaffold.
- Biofabrication with biopolymers and enzymes: potential for constructing scaffolds from soft matter.
- Redox-cycling and H2O2 generation by fabricated catecholic films in the absence of enzymes.
- LuxS coexpression enhances yields of recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli in part through posttranscriptional control of GroEL.
- Toxicogenomic response of Mycobacterium bovis BCG to peracetic acid and a comparative analysis of the M. bovis BCG response to three oxidative disinfectants.
- Biological nanofactories target and activate epithelial cell surfaces for modulating bacterial quorum sensing and interspecies signaling.
- Chitosan: an integrative biomaterial for lab-on-a-chip devices.
- Biofabrication to build the biology-device interface.
- Diffusion of interleukin-2 from cells overlaid with cytocompatible enzyme-crosslinked gelatin hydrogels.
- Synthetic analogs tailor native AI-2 signaling across bacterial species.
- Biological nanofactories facilitate spatially selective capture and manipulation of quorum sensing bacteria in a bioMEMS device.
- Engineered biological nanofactories trigger quorum sensing response in targeted bacteria.
- Autonomous induction of recombinant proteins by minimally rewiring native quorum sensing regulon of E. coli.
- Cross species quorum quenching using a native AI-2 processing enzyme.
- In situ generation of pH gradients in microfluidic devices for biofabrication of freestanding, semi-permeable chitosan membranes.
- A cantilever sensor with an integrated optical readout for detection of enzymatically produced homocysteine.
- Global transcriptomic response of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to chlorhexidine diacetate.
- Microarray analysis of Mycobacterium bovis BCG revealed induction of iron acquisition related genes in response to hydrogen peroxide.
- Quieting cross talk--the quorum sensing regulator LsrR as a possible target for fighting bacterial infections.
- Global transcriptome analysis of the Mycobacterium bovis BCG response to sodium hypochlorite.
- In vitro and in vivo RNA interference mediated suppression of Tn-caspase-1 for improved recombinant protein production in High Five cell culture with the baculovirus expression vector system.
- Chitosan-coated wires: conferring electrical properties to chitosan fibers.
- Biofabrication of antibodies and antigens via IgG-binding domain engineered with activatable pentatyrosine pro-tag.
- Plasmid-encoded protein: the principal factor in the "metabolic burden" associated with recombinant bacteria. Biotechnology Bioengineering, 1990.
- Towards area-based in vitro metabolic engineering: assembly of Pfs enzyme onto patterned microfabricated chips.
- Microbial nar-GFP cell sensors reveal oxygen limitations in highly agitated and aerated laboratory-scale fermentors.
- Orthogonal enzymatic reactions for the assembly of proteins at electrode addresses.
- Investigating apoptosis: characterization and analysis of Trichoplusia ni-caspase-1 through overexpression and RNAi mediated silencing.
- Block copolymer nanotemplating of tobacco mosaic and tobacco necrosis viruses.
- From unicellular properties to multicellular behavior: bacteria quorum sensing circuitry and applications.
- AI-2 biosynthesis module in a magnetic nanofactory alters bacterial response via localized synthesis and delivery.
- Toxicogenomic response of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to ortho-phenylphenol.
- Microarray analysis of toxicogenomic effects of ortho-phenylphenol in Staphylococcus aureus.
- Beyond silencing--engineering applications of RNA interference and antisense technology for altering cellular phenotype.
- Expression of green fluorescent protein in insect larvae and its application for heterologous protein production.
- On-line green fluorescent protein sensor with LED excitation.
- Design optimization for bioMEMS studies of enzyme-controlled metabolic pathways.
- Stochastic modeling of gene positive autoregulation networks involving signal molecules.
- Indole cell signaling occurs primarily at low temperatures in Escherichia coli.
- Chitosan fibers: versatile platform for nickel-mediated protein assembly.
- Programmable assembly of a metabolic pathway enzyme in a pre-packaged reusable bioMEMS device.
- Chitosan biotinylation and electrodeposition for selective protein assembly.
- Microarray analysis of toxicogenomic effects of triclosan on Staphylococcus aureus.
- Toxicogenomic response to chlorination includes induction of major virulence genes in Staphylococcus aureus.
- Methods for gene silencing with RNAi.
- Alternative bioreactor strategy for probing infection and production.
- Monitoring and visualization of baculovirus infection using green fluorescent protein strategy.
- Production of a recombinant antibody fragment in whole insect larvae.
- Protein assembly onto patterned microfabricated devices through enzymatic activation of fusion pro-tag.
- Comparative global transcription analysis of sodium hypochlorite, peracetic acid, and hydrogen peroxide on Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
- Transglutaminase crosslinked gelatin as a tissue engineering scaffold.
- Quorum sensing in Escherichia coli is signaled by AI-2/LsrR: effects on small RNA and biofilm architecture.
- Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli biofilms are inhibited by 7-hydroxyindole and stimulated by isatin.
- Metabolic engineering of the baculovirus-expression system via inverse "shotgun" genomic analysis and RNA interference (dsRNA) increases product yield and cell longevity.
- Magnetic nanofactories: localized synthesis and delivery of quorum-sensing signaling molecule autoinducer-2 to bacterial cell surfaces.
