Profile

Alexander Andrianov
Research Professor
Andrianov Group (240) 314-6456 aandrianov@umd.eduDr. Alexander Andrianov is a leader in the field of polyphosphazenes with a long-standing interest in applications of polymers for drug delivery systems and biomaterials. He has been involved in all aspects of technology development and commercialization, including product advancement from the research laboratory to manufacturing and clinical trials. Dr. Andrianov has served in various executive and managerial roles at a number of biotechnology companies focusing on drug delivery technologies and biomaterials, and he has worked as a biotechnology consultant to industrial, academic, and global health organizations.
CURRENT RESEARCH
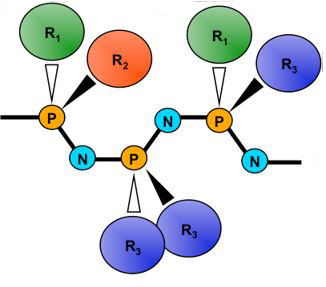
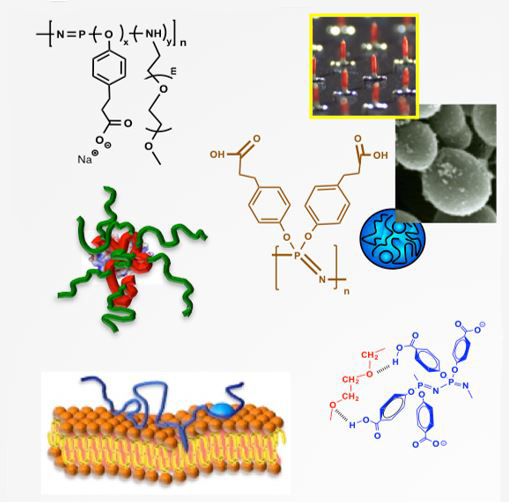
The Andrianov lab uses the polyphosphazene technology platform to develop novel materials for life sciences applications and studies interactions of these macromolecules with biologically important targets. Current projects include the development of potent macromolecular immunomodulators and vaccine delivery vehicles, biodegradable nanoparticulate drug delivery carriers with built-in ‘smart’ intracellular delivery functions, non-covalent PEGylation systems for extending protein half-life, and novel polyelectrolytes for aqueous layer-by-layer assembly of biocompatible, self-healing, fluorinated coatings.
The lab integrates expertise in rational design, controlled synthesis and scaled-up production of these macromolecules, as well as precise formulation and nanofabrication methods. It is equipped with state-of-the-art equipment and expertise for screening macromolecules for critical parameters such as biocompatibility and interactions with important protein targets.
Publications
- Rational design of flavivirus E protein vaccine optimizes immunogenicity and mitigates antibody dependent enhancement risk.
- Macromolecular dimensions of a synthetic polyelectrolyte as a factor in its interactions with protein and cells: desirability for longer chains.
- Polyphosphazene-Mediated Assembly of TLR4 and TLR7/8 Agonists Enables a Potent Nano-Adjuvant Delivery System for Hepatitis C Virus Vaccine Antigens.
- Cyclic Macromolecular Chains Visualized by Cryo-EM and AFM Reveal a Ring Expansion Polymerization Mechanism in a Classical Synthetic Pathway to Polyphosphazenes.
- Glycoengineering of the hepatitis C virus E2 glycoprotein improves biochemical properties and enhances immunogenicity.
- Glycoengineering of the hepatitis C virus E2 glycoprotein leads to improved biochemical properties and enhanced immunogenicity.
- Correction: Protein-polyelectrolyte complexation: effects of sterically repulsive groups, macromolecular architecture and hierarchical assembly.
- Delivery of protein therapeutics and vaccines using their multivalent complexes with synthetic polyelectrolytes.
- Virus-Mimicking Polymer Nanocomplexes Co-Assembling HCV E1E2 and Core Proteins with TLR 7/8 Agonist-Synthesis, Characterization, and In Vivo Activity.
- Protein-polyelectrolyte complexation: effects of sterically repulsive groups, macromolecular architecture and hierarchical assembly.
- Hydrolytically Degradable Zwitterionic Polyphosphazene Containing HEPES Moieties as Side Groups.
- Directly visualizing individual polyorganophosphazenes and their single-chain complexes with proteins.
- Nano-Assembled Polyphosphazene Delivery System Enables Effective Intranasal Immunization with Nipah Virus Subunit Vaccine.
- Engineering Degradation Rate of Polyphosphazene-Based Layer-by-Layer Polymer Coatings.
- Immunopotentiating Polyphosphazene Delivery Systems: Supramolecular Self-Assembly and Stability in the Presence of Plasma Proteins.
- A Biodegradable "one-for-all" Nanoparticle for Multimodality Imaging and Enhanced Photothermal Treatment of Breast Cancer.
- A biodegradable "one-for-all" nanoparticle for multimodality imaging and enhanced photothermal treatment of breast cancer.
- Monitoring Protein Complexation with Polyphosphazene Polyelectrolyte Using Automated Dynamic Light Scattering Titration and Asymmetric Flow Field Flow Fractionation and Protein Recognition Immunoassay.
- Prospects for developing an Hepatitis C virus E1E2-based nanoparticle vaccine.
- Fluorine-Functionalized Polyphosphazene Immunoadjuvant: Synthesis, Solution Behavior and In Vivo Potency.
- Noncovalent PEGylation of protein and peptide therapeutics.
- 4-Methylumbelliferone-Functionalized Polyphosphazene and Its Assembly into Biocompatible Fluorinated Nanocoatings with Selective Antiproliferative Activity.
- Skin Vaccination with Ebola Virus Glycoprotein Using a Polyphosphazene-Based Microneedle Patch Protects Mice against Lethal Challenge.
- Factors Controlling Degradation of Biologically Relevant Synthetic Polymers in Solution and Solid State.
- Polyphosphazene: A New Adjuvant Platform for Cocaine Vaccine Development.
- Hierarchically Structured, All-Aqueous-Coated Hydrophobic Surfaces with pH-Selective Droplet Transfer Capability.
- Induction of broadly neutralizing antibodies using a secreted form of the hepatitis C virus E1E2 heterodimer as a vaccine candidate.
- Cationic Fluoropolyphosphazenes: Synthesis and Assembly with Heparin as a Pathway to Hemocompatible Nanocoatings.
- Nano-Assembly of Quisinostat and Biodegradable Macromolecular Carrier Results in Supramolecular Complexes with Slow-Release Capabilities.
- Immunopotentiating and Delivery Systems for HCV Vaccines.
- Supramolecular assembly of Toll-like receptor 7/8 agonist into multimeric water-soluble constructs enables superior immune stimulation in vitro and in vivo.
- Intracellular Delivery of Active Proteins by Polyphosphazene Polymers.
- Improvement of RG1-VLP vaccine performance in BALB/c mice by substitution of alhydrogel with the next generation polyphosphazene adjuvant PCEP.
- Next generation polyphosphazene immunoadjuvant: Synthesis, self-assembly and in vivo potency with human papillomavirus VLPs-based vaccine.
- Design of a native-like secreted form of the hepatitis C virus E1E2 heterodimer.
- Polyphosphazenes enable durable, hemocompatible, highly efficient antibacterial coatings.
- Polyphosphazene immunoadjuvants: Historical perspective and recent advances.
- Structure-Based Design of Hepatitis C Virus E2 Glycoprotein Improves Serum Binding and Cross-Neutralization.
- In Vivo and In Vitro Potency of Polyphosphazene Immunoadjuvants with Hepatitis C Virus Antigen and the Role of Their Supramolecular Assembly.
- Molecular-Level Interactions of Polyphosphazene Immunoadjuvants and Their Potential Role in Antigen Presentation and Cell Stimulation.
- Self-assembly of polyphosphazene immunoadjuvant with poly(ethylene oxide) enables advanced nanoscale delivery modalities and regulated pH-dependent cellular membrane activity.
- Biodegradable Polyphosphazene Based Peptide-Polymer Hybrids.
- PCPP-formulated H5N1 influenza vaccine displays improved stability and dose-sparing effect in lethal challenge studies.
- Effect of environmental factors on hydrolytic degradation of water-soluble polyphosphazene polyelectrolyte in aqueous solutions.
- Protein stabilization in aqueous solutions of polyphosphazene polyelectrolyte and non-ionic surfactants.
- Microneedles with intrinsic immunoadjuvant properties: microfabrication, protein stability, and modulated release.
- Poly[di(sodium carboxylatoethylphenoxy)phosphazene] (PCEP) is a potent enhancer of mixed Th1/Th2 immune responses in mice immunized with influenza virus antigens.
- Degradation of polyaminophosphazenes: effects of hydrolytic environment and polymer processing.
- Synthesis, properties, and biological activity of poly[di(sodium carboxylatoethylphenoxy)phosphazene].
